Asset & Endpoint Management
Overview
Azure has several offerings to facilitate asset & configuration management including Azure Security Center, Azure Active Directory, Azure AD Privileged Identity Management, Azure Policy and Azure Information Protection
-
Azure Security Center is a unified infrastructure security management system that strengthens the security posture of your data centers and provides advanced threat protection across your hybrid workloads in the cloud – whether they’re in Azure or not – as well as on premises.
-
Azure Active Directory is an identity and access management-as-a-service (IDaaS) solution that combines single-on capabilities to any cloud and on-premises application with advanced protection.
-
Azure AD Privileged Identity Management is a service that enables you to manage, control, and monitor access to important resources in your organization. These resources include resources in Azure AD, Azure, and other Microsoft Online Services like Office 365 or Microsoft Intune.
-
Azure Information Protection helps secure email, documents, and sensitive data that you share outside your company.
Protect Confidential Data
Bitlocker Drive Encryption
BitLocker Drive Encryption is a data protection feature that integrates with the operating system and addresses the threats of data theft or exposure from lost, stolen, or inappropriately decommissioned computers.
BitLocker provides the most protection when used with a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) version 1.2 or later. The TPM is a hardware component installed in many newer computers by the computer manufacturers. It works with BitLocker to help protect user data and to ensure that a computer has not been tampered with while the system was offline.
Security Baseline: All enrolled Windows 10/11 devices are configured to silently deploy Bitlocker Drive Encryption to meet FIPS requirements. Settings can be located in
NIST - Endpoint Protection Configuration Profile.
Sensitivity Labels
You can secure controlled unclassified information (CUI) and control information flows with Azure Information Protection (AIP). Azure Information Protection is a cloud-based solution that helps your organization organization to classify and optionally, protect its documents and emails by applying labels.
Security Baseline: There are 2 sensitivity labels created as part of your security baseline.
CUI Encrypt Only- Encrypts e-mails and files internal to the company’s domain. The scope included in this policy contains files and emails, and will encrypt, as well as mark the contents of the files. Users are able to assign permissions at the time of label application. In MS Outlook, e-mails are encrypted and forwarding disabled only. By default, a water mark (specified at the time of onboarding) will be applied.
CUI Do Not Forward- Encrypts and prohibits forwarding of e-mails with this label attached when sending to anywhere external to the company’s domain. In MS Outlook, e-mails are encrypted and forwarding disabled only. By default, a water mark (specified at the time of onboarding) will be applied.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
Data loss prevention helps to protect sensitive company data and reduce risk of data leakage, by preventing users from inappropriately sharing it with people who should not have.
Security Baseline: The following data loss prevention policies are implemented to help identify, monitor, and automatically protect sensitive items
- Default policy for Teams
This policy detects the presence of credit card numbers in Teams chats and channel messages. When this sensitive info is detected, admins will receive an alert but policy tips won’t be displayed to users. You can edit these actions at any time.- Locations to apply the policy: Teams chat and channel messages
- Policy settings: Default Teams DLP policy rule
NIST - DLP Policy
Helps detects the presence of information commonly considered to be personally identifiable information (PII) in the United States, including information like social security numbers or passport numbers.- Locations to apply the policy: Exchange email, SharePoint sites, OneDrive accounts, Teams chat and channel messages
- Policy settings: Low volume of content detected U.S. PII, High volume of content detected U.S. PII
NIST - CUI Sensitivity Label
Blocks the sharing of all OneDrive, Sharepoint & Emails assigned with CUI sensitivity label outside of organization. Policy allows for override with justification.- Locations to apply the policy: Exchange email, SharePoint sites, OneDrive accounts
- Policy settings: CUI Sensitivity Label (Allow Override)
Conditional Access Policies
Conditional access policies are implemented to limit access to data from unmanaged devices. Unmanaged devices are considered any device that is not enrolled OR any device that is not compliant based on the assigned compliance policies in this baseline security configuration.
Security Baseline: The following conditional access policies have been configured to limit data accessed by unmanaged devices.
NIST - GRANT - Require compliant device for Windows or Mac access- Requires an enrolled and compliant Windows or Mac device to access corporate data within Office 365[SharePoint admin center]Block access from apps on unmanaged devices- Unmanaged devices are allowed limited, web-only access to Sharepoint data.[SharePoint admin center]Use app-enforced Restrictions for browser access- Unmanaged devices accessing data via web browser are automatically signed out after 15 minutes of inactivity
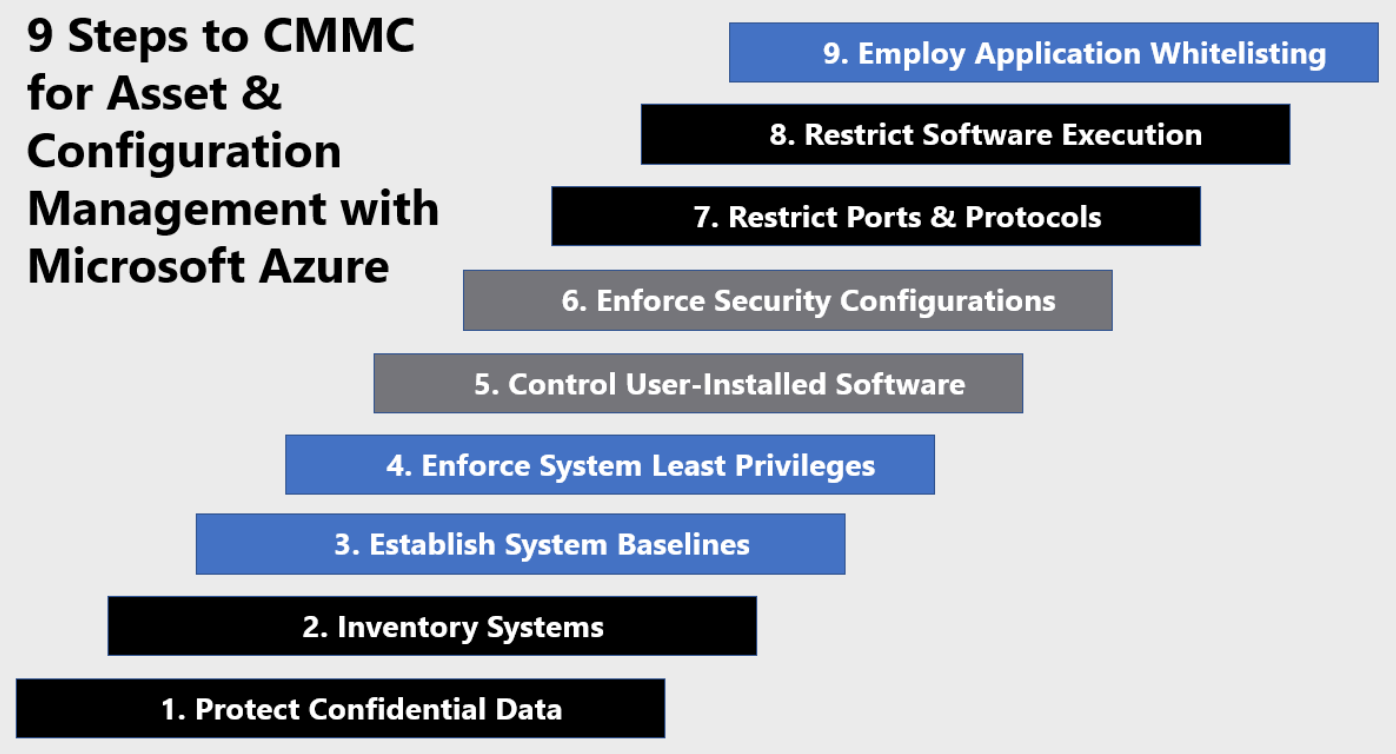
Inventory Systems
Microsoft Endpoint Manager (Intune) allows your organization the ability to inventory all onboarded devices. Browse to the endpoint manager (GCC / Commercial: https://endpoint.microsoft.com, GCC High: https://endpoint.microsoft.us) and navigate to Devices>All Devices.
- Overview shows device name, and lists key properties of the device. With GCC commercial, there is the ability to perform the following actions on the device: retire, wipe, delete, remote lock, sync, reset passcode, restart, fresh start, autopilot reset, quick scan, full scan, update windows defender security intelligence, bitlocker key rotation, rename device, new remote assistance session (devices with a ‘*’ require the device to be onboarded in AutoPilot). Some of these items are currently limited in the GCC high cloud due to AutoPilot not being an available feature.
- Properties can be used to assign device categories. This would be used to designate bring your own vs. corporate owned devices.
- Hardware includes many details about the device, like device ID, operating system and version, storage space, and various other hardware related details.
- Discovered apps allows the administrator to see what apps MEM / Intune has discovered on the device, along with their versions. For more information: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/apps/app-discovered-apps
- Device compliance and device configuration will show all assigned compliance/configuration profiles that have been assigned to the device(s) along with whether the policies have succeeded or failed.
- Recovery Keys shows available BitLocker keys found for the device.
- Managed apps lists all managed apps that Microsoft Endpoint Manager / Intune have configured and deployed to the device.

- More information: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/remote-actions/device-inventory
Establish Baselines
Nimbus Logic has implemented the Microsoft best practices configuration(s) based on the NIST 800-171 R2 assessment template provided by Microsoft to your company’s tenant. This includes the manually configured and maintained configurations provided by Nimbus Logic, as well as the pre-configured and tested controls implemented by Microsoft. The assessment template used contains the controls and action data needed to track compliance with regulations, standards, and policies.
- Overview
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) 800-171 addresses the requirements for the protection of control unclassified information (CUI) stored in nonfederal systems and organizations. This framework provides agencies with recommended security requirements for protecting the confidentiality of CUI when the information is stored in nonfederal systems and organizations, when the nonfederal organization is not collecting or maintaining information on behalf of a federal agency or using or operating a system on behalf of an agency, and where there are no specific safeguarding requirements for protecting the confidentiality of CUI. - Baseline Configuration
Any devices that are joined to your company’s Azure Active Directory instance will be managed by Endpoint Manager/Intune. The All Employees group is assigned all configuration and compliance policies by default. User / group specific configurations will be applied based on assignments created at the time of onboarding / new user additions. These baseline configuration and compliance policies are what drive your company’s compliance, and alert both the Compliance Alerts users in your company, and when help and/or incident response is required by the CSP, opens a ticket with the Nimbus Logic Government Helpdesk.
Enforce System Least Privilege
The principle of least privilege is defined as a security architecture that is designed so that each entity is granted the minimum system resources and authorizations that the entity needs to perform its function.
- Managed Identities in Azure Active Directory
- This configuration employs the concept of least privilege, allowing only those authorized accesses necessary to accomplish assigned tasks necessary for organizational missions and business functions in compliance with your organization’s policies. Access Control policies include processes for employing the concept of least privilege, and for authorizing user/software/application access based on the principle of least privilege. This configuration enables self-service password reset (SSPR) in Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) to give users the ability to change or reset their password with no administrator or help desk involvement (https://passwordreset.activedirectory.windowsazure.us/).
- The following access controls principles have been established via Role Based Access Control (RBAC): designing access control thoroughly, forcing all requests to go through access control checks, denying access by default, implementing the principle of least privilege, avoiding hard-coding roles, and logging all access control events.
- Privileged Identity Management
Privileged Identity Management allows users to check what roles they are eligible for, and request them as needed. This also allows the specified “approver” to approve or deny the access request. Users can check their access any time at GCC Commercial https://myaccess.microsoft.com, GCC High: https://myaccess.microsoft.us. It is important to note that these access assignments can be configured for a specified duration, or enabled/disabled manually by a user with the appropriate permissions.
Control User-Installed Software
Application Whitelisting along with Privileged Identity Management (PIM) are both implemented to assist in the governance of endpoint application usage and installations.
- AppLocker
At the time of onboarding, your company specified a pre-determined list of allowed applications. Applications can be added to the AppLocker whitelist. These requests would be sent to the CSP after being approved by your company’s endpoint / user administrator. - Company Portal
Generally, there will be a pre-configured list of approved software available for download and install without any need to elevate privileges or attain permission in your Company Portal App. - Privileged Identity Management
Privileged Identity Management can be implemented to allow a user the Application Administrator role, granting them temporary permission to install software locally on their endpoint. It’s important to note that this application would also need to be whitelisted and added to AppLocker policies in order to run successfully.
Enforce Security Configurations
Security configurations are enforced by use of Compliance policies managed in the Microsoft Endpoint Manager portal. Compliance policies define the rules and settings that users and devices must meet to be compliant. Enrolled devices are continually scanned to validate that they are meeting the security baselines defined within the CAAS documentation. If a device falls out of compliance, it has a 7 day grace period to come back into compliance or otherwise lose access to corporate data.
Security Baseline: Once a device falls out of compliance, there is a 7 day grace period to remediate the issue and bring the device back into a compliant state. A support ticket will automatically be raised with Nimbus Logic Government support to investigate the issue and a Nimbus Logic support technician will work with the user to remediate any compliance issues associated with the user or device.
Restrict Ports & Protocols
The Endpoint Manager configuration implemented by Nimbus Logic specifically limits the protocols available to use for external communication to using SSL 3.0/TLS 1.2. This prevents unencrypted data transmission to and from the Microsoft cloud. Port limitations can be added to your internal network via your firewall, but are not locked down via your Compliance as a Service configuration due to the nature of the service (being fully in the cloud). Specific ports can be blocked at your request any time via support ticket (email support@nimbus-logic.us).
Security Baseline: Protocol limitation are defined in the Configuration Profile
NIST - Security Protocolsdevice configuration profile.
Restrict Software Execution
Applocker policies are enforced to deny all EXE and DLL execution unless otherwise whitelisted
Employ Application Whitelisting
AppLocker
Applying application whitelisting is an effective control to prevent malicious application execution. AppLocker is implemented on your tenant and used to control the following file types:
- Executables: exe and com files
- The baseline configuration for EXE & COM files allows all members of the local administrators group to run all applications. By default, members of the “Everyone” group can run applications that are located in the Programs Files folders. Standard users are also able to execute files in the Windows folder - which allows for normal day to day activities in the operating system.
- Other default whitelisted applications include programs that are signed and published by Microsoft and Adobe.
- Scripts: js, ps1, vbs, cmd and bat files
- By default members of the local Administrators group are able to run all scripts. Members of the Everyone group are able to run scripts from the folders required for day to day operations (e.g. Program Files, Windows).
- Windows Installer files: msi and msp files
- By default members of the local Administrators group are able to run Windows installer files.
- Dynamic-link-libraries: dll and ocx
- By default members of the local Administrators group are able to run DLL files.
- Members of the Everyone group are allowed to run DLLs in the MS Windows folders.
- DLLs that call on older versions of PowerShell are explicitly denied (implicitly allowing 10.* and above).
- Packed app Rules (Windows Store): Appx (Windows 10 only)
- Only apps that are signed and published by Microsoft are available for download from the Microsoft Store.
AppLocker also assists your organization in maintaining:
- Application Inventory
Keep a maintained list of all allowed and blocked software in your company. This is established at the time of onboarding, but will also be an evolving document as requirements change. - Protection against unwanted software
If an application is not specifically identified by its publisher, installation path, or file hash, the attempt to run the application fails. This prevents unintentional installation of malware and/or any other unwanted software. - Software standardization
Policies can be configured to allow only supported or approved applications to run on computers within a business group, or by version / release. This permits a more uniform application deployment and usage scenario, and would also be defined in your whitelisted application(s) documents.
Security Baseline: AppLocker policies are enforced and defined in the device configuration profile,
NIST - AppLocker Policies
Controlled Folder Access
Controlled folder access works by only allowing trusted apps to access protected folders. Protected folders are specified when controlled folder access is configured. Typically, commonly used folders, such as those used for documents, pictures, downloads, and so on, are included in the list of controlled folders.
Controlled folder access works with a list of trusted apps. Apps that are included in the list of trusted software work as expected. Apps that are not included in the list are prevented from making any changes to files inside protected folders.
Apps are added to the list based upon their prevalence and reputation. Apps that are highly prevalent throughout your organization and that have never displayed any behavior deemed malicious are considered trustworthy. Those apps are added to the list automatically.
Security Baseline: Controlled folder access is enabled in the Configuration Profile
NIST - Endpoint Protection Configuration Profile
Microsoft Defender SmartScreen
Microsoft Defender SmartScreen protects against phishing or malware websites and applications, and the downloading of potentially malicious files.
Microsoft Defender SmartScreen determines whether a site is potentially malicious by:
-
Analyzing visited webpages looking for indications of suspicious behavior. If Microsoft Defender SmartScreen determines that a page is suspicious, it will show a warning page to advise caution.
-
Checking the visited sites against a dynamic list of reported phishing sites and malicious software sites. If it finds a match, Microsoft Defender SmartScreen shows a warning to let the user know that the site might be malicious.
Microsoft Defender SmartScreen determines whether a downloaded app or app installer is potentially malicious by:
-
Checking downloaded files against a list of reported malicious software sites and programs known to be unsafe. If it finds a match, Microsoft Defender SmartScreen shows a warning to let the user know that the site might be malicious.
-
Checking downloaded files against a list of files that are well known and downloaded by many Windows users. If the file isn’t on that list, Microsoft Defender SmartScreen shows a warning, advising caution.
Security Baseline: Defender Smartscreen is enabled in the configuration profile
NIST - Endpoint Protection Configuration Profile
