Recovery & Risk Management
Azure has several offerings to facilitate recovery & risk management including Azure Backup, Azure Security Center, Azure Sentinel and the Microsoft Graph Security API.
-
Azure Backup facilitates backups for Azure Virtual Machines, SQL workloads, and on-premises VMware machines without additional infrastructure. Encrypt data and keep it for extended periods, even after legitimate deletion, through multifactor authentication.
-
Azure Security Center is a unified infrastructure security management system that strengthens the security posture of your data centers, and provides advanced threat protection across your hybrid workloads in the cloud – whether they’re in Azure or not – as well as on premises.
-
Microsoft 365 Defender is a unified pre- and post-breach enterprise defense suite that natively coordinates detection, prevention, investigation, and response across endpoints, identities, email, and applications to provide integrated protection against sophisticated attacks.
-
Microsoft Sentinel is a scalable, cloud-native, security information event management (SIEM) and security orchestration automated response (SOAR) solution.
-
Microsoft Graph Security API simplifies integration with Microsoft and third-party security solutions. Using one endpoint, one software development kit (SDK), one schema, and one authentication mechanism, customers and partners can easily build integrated security applications, workflows and analytics.
Backups & Data Retention
Regular backups ensure continuity and availability in the event of a disaster.
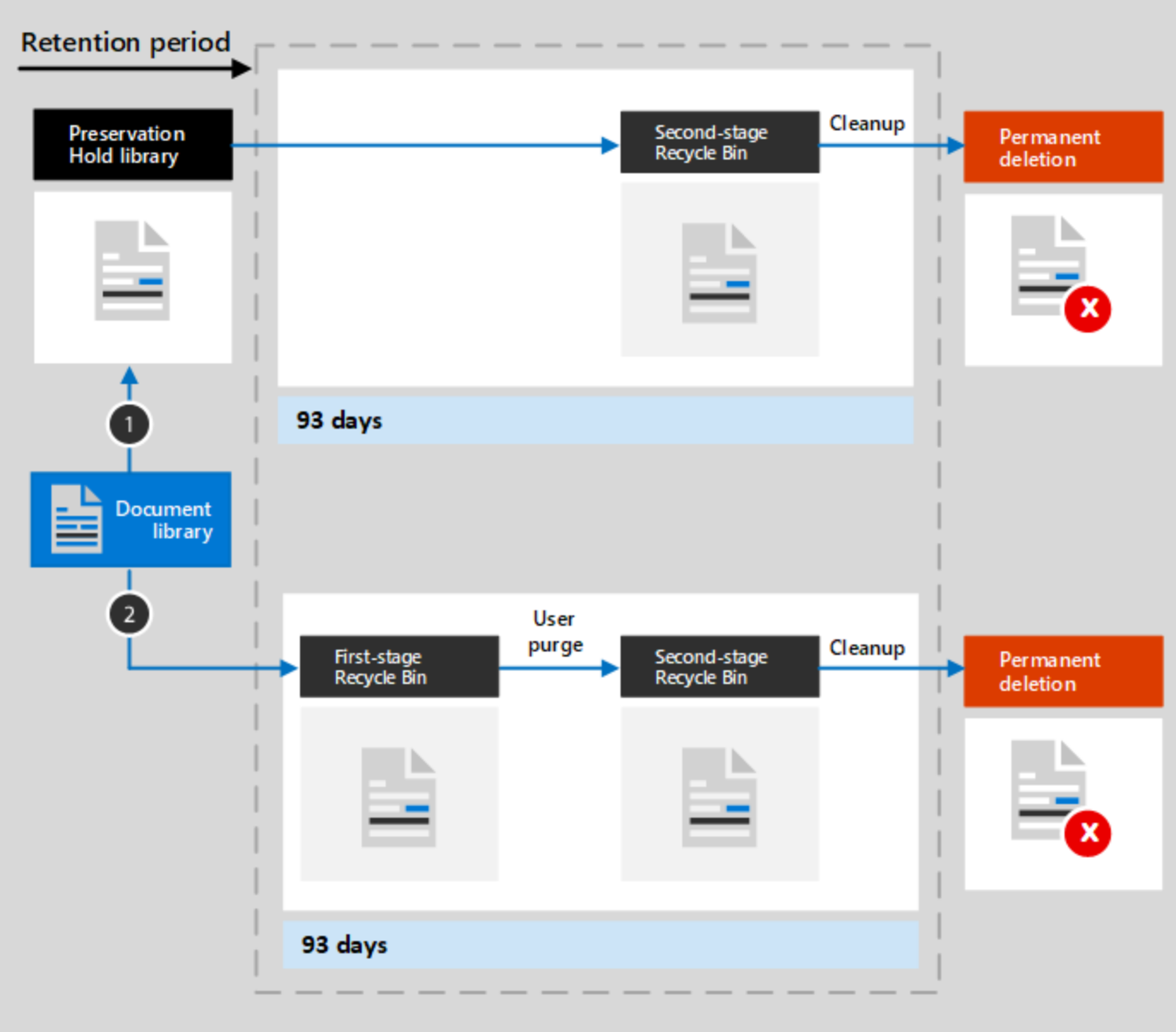
Security Baseline: Storing files in Sharepoint Online document libraries allows for a 30 day recovery of any deleted files along with document versioning that tracks modifications to data.
Data Retention Policies
The implemented configuration enables file versioning and utilizes data retention for Sharepoint and Onedrive through a Preservation Hold library.
When a user changes or deletes an item that’s subject to retention, a check is made whether the content has been changed since the retention settings were applied. If this is the first change since the retention settings were applied, the content is copied to the Preservation Hold library, which allows the user to change or delete the original content.
Security Baseline: OneDrive & Sharepoint document libraries have been configured to be automatically assigned retention labels
Azure Backup
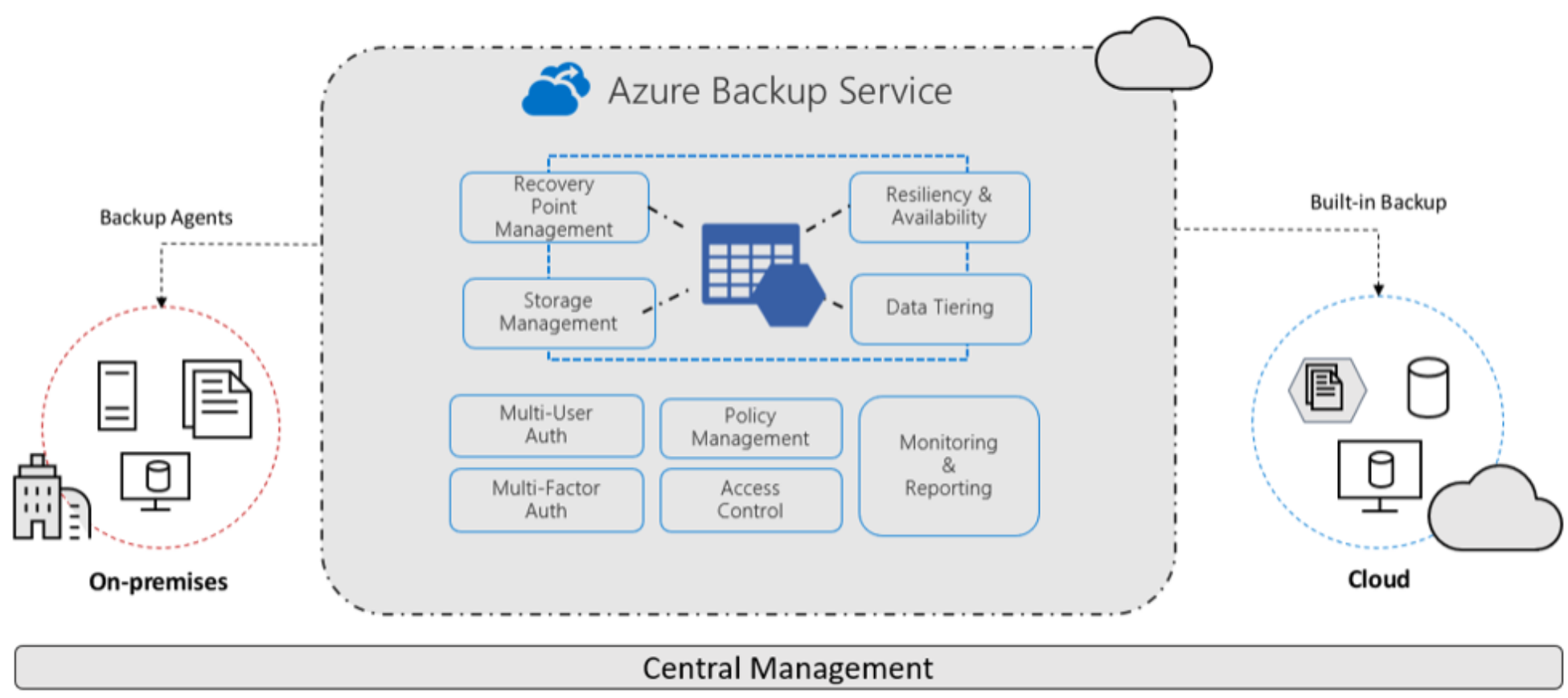
For files not stored in OneDrive or Sharepoint online, Azure Backup can optionally be configured to provide a cloud-based backup service for on-premise systems, files, Azure VMs, file shares & databases.
Protect Backups
There are several methods to protecting backups including access management, redundancy and encryption. Azure Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) enables fine-grained access management for Azure. Using RBAC, you can segregate duties within your team and grant only the amount of access to users that they need to perform their jobs. Azure Backup provides three built-in roles to control backup management operations. For more information, see Use Role-Based Access Control to manage Azure Backup recovery points.
- Backup Contributor: This role has all permissions to create and manage backup except deleting Recovery Services vault and giving access to others. Imagine this role as admin of backup management who can do every backup management operation.
- Backup Operator: This role has permissions to everything a contributor does except removing backup and managing backup policies. This role is equivalent to contributor except it can’t perform destructive operations such as stop backup with delete data or remove registration of on-premises resources.
- Backup Reader: This role has permissions to view all backup management operations. Imagine this role to be a monitoring person.
Validate Backup Facilities
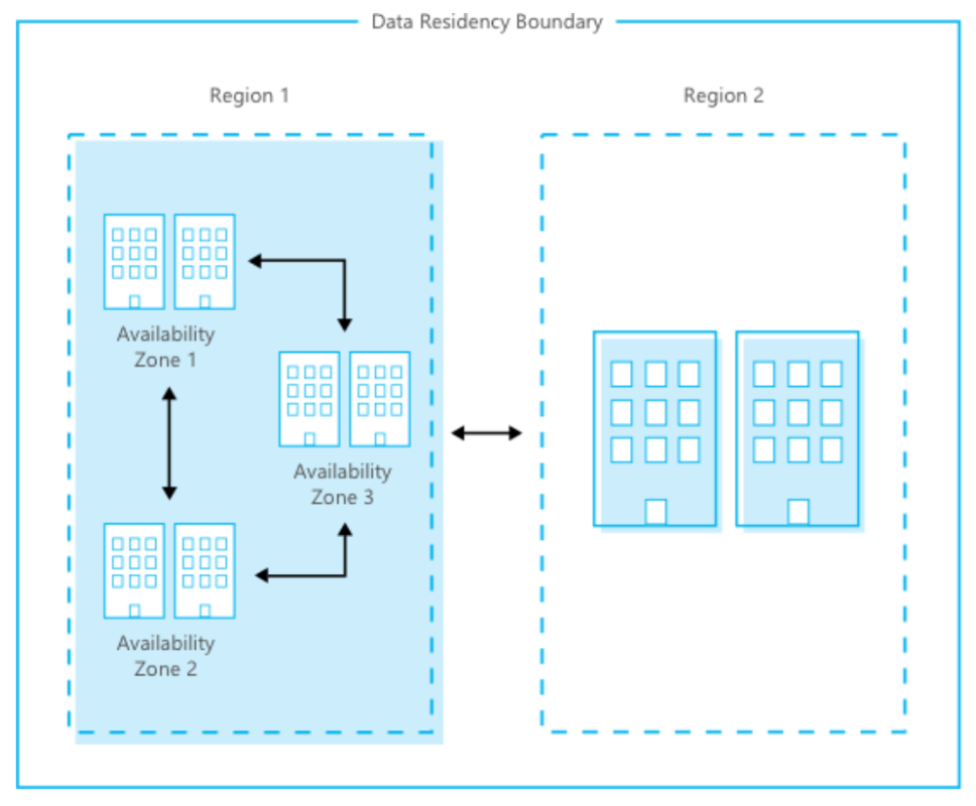
Azure backups are distributed through Azure data centers which adhere to strict standards of confidentiality, integrity and availability. Azure is composed of a globally distributed datacenter infrastructure, supporting thousands of online services and spanning more than 100 highly secure facilities worldwide. Azure has 52 regions worldwide and is available in 140 countries/regions.
The Microsoft Cloud Infrastructure and Operations team designs, builds, operates, and improves the security of the cloud infrastructure. This team ensures that the Azure infrastructure is delivering high availability and reliability, high efficiency, and smart scalability. The team provides a more secure, private, and trusted cloud.
Uninterruptible power supplies and vast banks of batteries ensure that electricity remains continuous if a short-term power disruption occurs. Emergency generators provide backup power for extended outages and planned maintenance. If a natural disaster occurs, the datacenter can use onsite fuel reserves.
High-speed and robust fiber optic networks connect datacenters with other major hubs and internet users. Compute nodes host workloads closer to users to reduce latency, provide geo-redundancy, and increase overall service resiliency. A team of engineers works around the clock to ensure services are persistently available.
Microsoft ensures high availability through advanced monitoring and incident response, service support, and backup failover capability. Geographically distributed Microsoft operations centers operate 24/7/365. The Azure network is one of the largest in the world. The fiber optic and content distribution network connect datacenters and edge nodes to ensure high performance and reliability.
-
Disaster Recovery: Azure keeps your data durable in two locations. You can choose the location of the backup site. In both locations, Azure constantly maintains three healthy replicas of your data.
-
Database Availability: Azure ensures that a database is internet accessible through an internet gateway with sustained database availability. Monitoring assesses the health and state of the active databases at five-minute time intervals.
-
Storage Availability: Azure delivers storage through a highly scalable and durable storage service, which provides connectivity endpoints. This means that an application can access the storage service directly. The storage service processes incoming storage requests efficiently, with transactional integrity. For more information, see Azure infrastructure availability.
